
Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 Laser Fusion Research Center, China Academy of Engineering Physics, Mianyang, Sichuan 621900, People’s Republic of China
2 Institute of Applied Physics and Computational Mathematics, Beijing 100094, People’s Republic of China
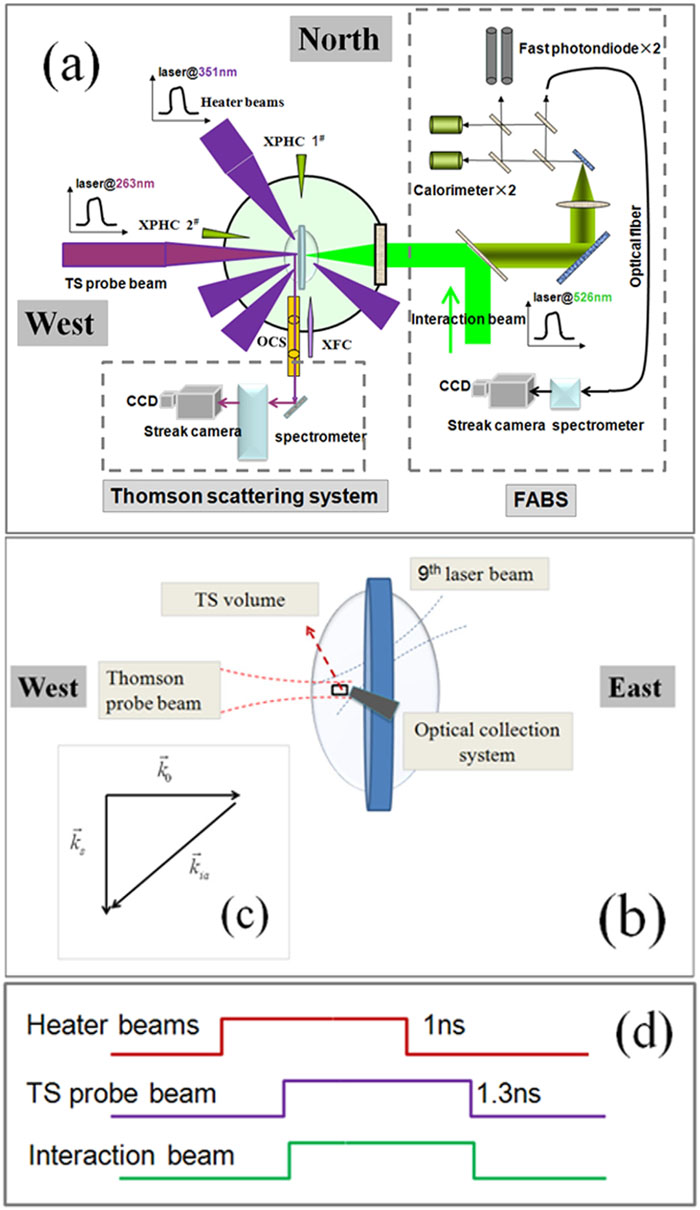
In an experiment performed on the Shenguang-III prototype laser facility, collective Thomson scattering (TS) is used to study the spatial growth of stimulated Brillouin scattering (SBS) in a gas-filled hohlraum by detecting the SBS-driven ion acoustic wave. High-quality time-resolved SBS and TS spectra are obtained simultaneously in the experiment, and these are analyzed by a steady-state code based on the ray-tracing model. The analysis indicates that ion–ion collisions may play an important role in suppressing SBS growth in the Au plasma; as a result, the SBS excited in the filled gas region is dominant. In the early phase of the laser pulse, SBS originates primarily from the high-density plasma at the edges of the interaction beam channel, which is piled up by the heating of the interaction beam. Throughout the duration of the laser pulse, the presence of the TS probe beam might mitigate SBS by perturbing the density distribution around the region overlapping with the interaction beam.
Matter and Radiation at Extremes
2024, 9(2): 027601

Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 Institute of Applied Physics and Computational Mathematics, Beijing 100094, China
2 Laser Fusion Research Center, China Academy of Engineering Physics, Mianyang, Sichuan 621900, China
3 HEDPS, Center for Applied Physics and Technology, and College of Engineering, Peking University, Beijing 100871, China
The first laser–plasma interaction experiment using lasers of eight beams grouped into one octad has been conducted on the Shenguang Octopus facility. Although each beam intensity is below its individual threshold for stimulated Brillouin backscattering (SBS), collective behaviors are excited to enhance the octad SBS. In particular, when two-color/cone lasers with wavelength separation 0.3 nm are used, the backward SBS reflectivities show novel behavior in which beams of longer wavelength achieve higher SBS gain. This property of SBS can be attributed to the rotation of the wave vectors of common ion acoustic waves due to the competition of detunings between geometrical angle and wavelength separation. This mechanism is confirmed using massively parallel supercomputer simulations with the three-dimensional laser–plasma interaction code LAP3D.
Matter and Radiation at Extremes
2023, 8(5): 055602

Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 Institute of Applied Physics and Computational Mathematics, Beijing 100094, China
2 Research Center of Laser Fusion, China Academy of Engineering Physics, Mianyang 621900, China
3 Graduate School, China Academy of Engineering Physics, Beijing, China
4 HEDPS, Center for Applied Physics and Technology, and College of Engineering, Peking University, Beijing 100871, China
A recently proposed octahedral spherical hohlraum with six laser entrance holes (LEHs) is an attractive concept for an upgraded laser facility aiming at a predictable and reproducible fusion gain with a simple target design. However, with the laser energies available at present, LEH size can be a critical issue. Owing to the uncertainties in simulation results, the LEH size should be determined on the basis of experimental evidence. However, determination of LEH size of an ignition target at a small-scale laser facility poses difficulties. In this paper, we propose to use the prepulse of an ignition pulse to determine the LEH size for ignition-scale hohlraums via LEH closure behavior, and we present convincing evidence from multiple diagnostics at the SGIII facility with ignition-scale hohlraum, laser prepulse, and laser beam size. The LEH closure observed in our experiment is in agreement with data from the National Ignition Facility. The total LEH area of the octahedral hohlraum is found to be very close to that of a cylindrical hohlraum, thus successfully demonstrating the feasibility of the octahedral hohlraum in terms of laser energy, which is crucially important for sizing an ignition-scale octahedrally configured laser system. This work provides a novel way to determine the LEH size of an ignition target at a small-scale laser facility, and it can be applied to other hohlraum configurations for the indirect drive approach.
Matter and Radiation at Extremes
2022, 7(6): 065901
中国工程物理研究院激光聚变研究中心, 四川 绵阳 621900
为了在输出能量为100 kJ的激光装置集束平台上开展激光等离子体不稳定性(LPI)实验研究,建设了基于集束构型的散射光诊断系统。该诊断系统使用漫反射板作为主要拦光、反射、取样元件,利用成像方式将散射光分别成像至iCCD(intensifier Charge Coupled Device)相机等记录部件,采取取样测量方式得到散射光的空间分布、能量大小、光谱及时间波形等。在集束物理实验中,该系统获得了较完备的物理数据,与物理模拟计算程序的计算结果较为吻合,表明在当前条件下散射光的主要机制为子束机制,其作用过程主要集中于等离子体未排空的前期。
激光光学 散射光 漫反射板 成像 几何光学
Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 Research Center of Laser Fusion, China Academy of Engineering Physics, Mianyang, Sichuan 621900, People’s Republic of China
2 Institute of Applied Physics and Computational Mathematics, Beijing 100088, People’s Republic of China
3 CAS Key Laboratory of Geospace Environment and Department of Engineering and Department of Engineering and Applied Physics, University of Science and Technology of China, Hefei, Anhui 230027, People’s Republic of China
We report experimental research on laser plasma interaction (LPI) conducted in Shenguang laser facilities during the past ten years. The research generally consists of three phases: (1) developing platforms for LPI research in mm-scale plasma with limited drive energy, where both gasbag and gas-filled hohlraum targets are tested; (2) studying the effects of beam-smoothing techniques, such as continuous phase plate and polarization smoothing, on the suppression of LPI; and (3) exploring the factors affecting LPI in integrated implosion experiments, which include the laser intensity, gas-fill pressure, size of the laser-entrance hole, and interplay between different beam cones. Results obtained in each phase will be presented and discussed in detail.
Matter and Radiation at Extremes
2019, 4(5): 055202
1 中国工程物理研究院 激光聚变研究中心, 四川 绵阳 621900
2 北京应用物理与计算数学研究所, 北京 100088
六通黑腔是我国独立自主设计的新型激光惯性约束聚变驱动腔型。在大型激光装置上采用全束组注入方式, 首次获得了新型六通黑腔10~20倍收缩比综合内爆完整配套实验数据, 实现最高YOC2D(实验产额/二维模拟产额)达80.4%的综合内爆性能。
激光间接驱动 六通黑腔 内爆 laser indirect-driven six-port-cylindrical hohlraum implosion 强激光与粒子束
2018, 30(11): 110101
中国工程物理研究院激光聚变研究中心, 四川 绵阳 621900
在超短脉冲抽运光作用下,利用双光子激发研究了多晶金刚石非线性吸收和非线性折射的动力学演化过程。在非线性吸收动力学实验中,观察到了金刚石样品中被激发载流子的两个不同的复合过程,时间尺度分别在百皮秒量级和纳秒量级,精确得到了不同抽运光能量作用时两个过程各自的时间常数。在非线性折射动力学实验中,观察到了金刚石样品中由非简并双光子吸收过程所引起的正的非线性折射率变化,得到了样品的三阶非线性系数。
非线性光学 双光子吸收 飞秒抽运探测 多晶金刚石 相位物体
Author Affiliations
Abstract
The Key Laboratory of Weak Light Nonlinear Photonics, Ministry of Education of China, Nankai University, Tianjin 3004572 Photonics Center, College of Physics Science, Nankai University, Tianjin 3000713 Institute of Fluid Physics, China Academy of Engineering Physics, Mianyang 621900
2 Nonvolatile two-color holographic recording gated by incoherent ultraviolet (UV) light centered at 365 nm is investigated in near-stoichiometric lithium niobate crystals. The influence of thermal treatment on the two-color recording is studied. The results show that thermal reduction tends to improve the two-color recording performance, whereas thermal oxidation degrades the two-color recording. With an incoherent 0.2-W/cm2 UV gating light and a 0.25-W/cm2 semiconductor recording laser at 780 nm, a two-color recording sensitivity of 4\times10^{-3} cm/J and a recording dynamic range characterized by M/# of 0.12 are achieved in a 2.2-mm thermally reduced near-stoichiometric lithium niobate crystal. We attribute the improvement to the prolonged lifetime of small polarons and the increased absorption at the gating wavelength due to thermal reduction.
铌酸锂 热处理 全息存储 非挥发 210.2860 Holographic and volume memories 090.2900 Optical storage materials 160.2900 Optical storage materials 160.5320 Photorefractive materials Chinese Optics Letters
2009, 7(1): 0167
中南民族大学激光光谱应用实验室, 湖北 武汉 430074
应用激光击穿光谱法(LIBS)探测了体液中各种物质的含量。脉冲Nd:YAG激光器产生的波长1064 nm的激光束(脉宽10 ns,重复频率10 Hz,激光能量约300 mJ)经凸透镜聚焦后,击穿模拟体液(质量分数为10%葡萄糖和0.9%NaCl的混合水溶液)产生激光等离子体,利用中阶梯光谱仪和像增强CCD(ICCD)探测其光谱信号,开展相应的激光击穿光谱研究。实验结果表明应用激光击穿光谱的技术完全可以同时检测出溶液中的有机物(葡萄糖)和金属离子,而且金属离子的检测灵敏度明显优于有机物,各待测物质的特征谱线强度与其含量存在指数关系。该方法为体液中微量元素的精确测量提供了实验依据。
光谱学 光谱分析 激光击穿光谱 葡萄糖溶液 NaCl溶液





